Sustainability
Sustainability Strategy
Prysmian’s sustainability strategy
The sustainability strategy is based on four pillars, each of which contributes to the creation of value added and allows for the implementation of long-term plans focusing on sustainability, including financial, for the benefit of the Group and all of its stakeholders.

The central role played by sustainability in Prysmian's strategy is also evident from the definition of a specific type of governance , which is responsible for overseeing all Group initiatives in a structured and rigorous manner and ensuring their alignment with ESG targets.

Prysmian is committed to reducing the negative impact on the environment during its manufacturing and installation activities and acts directly on the design and configuration of its products and solutions, helping to facilitate decarbonization along its value chain. Prysmian holds a leadership role in its supply chain by promoting virtuous practices with all its partners.

Prysmian places people at the center of its activities. This commitment is reflected both in employee initiatives (e.g., promoting work-life balance, diversity, inclusion, training) and in supporting the social communities in which the company operates.

Innovation is an indispensable element in achieving the sustainability goals of Prysmian, which has always invested in research and development to offer low-impact, high-efficiency products. The commitment to innovative solutions continues; sustainability is one of the key drivers of Prysmian's research and development strategy, reflected in the new "design for sustainability" concept.
The 4 main topics for Prysmian
Climate
Our commitment to climate is realized through a structured and ambitious strategy: the Prysmian Climate Ambition. We have set clear and measurable goals, based on science and in line with the Paris Agreement, with the aim of reducing greenhouse gas emissions throughout our value chain. Together, we are building a low-emission future through concrete and responsible actions. By leveraging the Science-Based Targets initiative (SBTi), we guarantee that our approach remains credible and aligned with global best practices.
Goals
Scope 1 and 2 Market Based GHG emissions reduction vs baseline 2019 by 2030
Scope 3 GHG emissions reduction vs baseline 2019 by 2030
Acceleration of the Net Zero target along the entire value chain by 2035 1
2024 Results
Scope 1 and 2 Market Based GHG emissions reductions vs. baseline 2019
Scope 3 GHG emissions reduction vs baseline 2019 2
2 The value has been updated from what was published in the 2024 Integrated Annual Report following SBTi validation, received after the Report's publication, which includes: the restatement of the 2019 baseline with the inclusion of Encore Wire and the update of the emission factors of the power grids.
Circular Economy
As we strive to a more sustainable future, we resolutely embrace the principles of circular economy, transforming the way we use resources and reducing waste. This means rethinking the entire product life cycle, from the use of recycled materials to designing more sustainable solutions and to responsible waste management. We are constantly investing in innovation to develop cables, components and solutions with reduced environmental impact, prioritizing recyclable raw materials and more efficient production processes, reducing the consumption of virgin resources, enhancing industrial waste recycling, and collaborating with suppliers and customers.
Goals
Revenues from sustainable solutions by 2028.
Recycled content on PE and copper jackets by 2025.
2024 Results
Revenues from sustainable solutions by 2028.
Recycled content on PE and copper jackets by 2025.
Biodiversity
At Prysmian, we believe that biodiversity is not only about species conservation, but is critical to ensuring the long-term sustainability of the natural resources on which our operations are based. In an ever-changing world, protecting ecosystems is not only a responsibility, but an opportunity to make our processes more resilient and efficient.
Goals
Net-Gain by 2035: adoption of strategies and practices aimed at improving biodiver-sity overall in all priority areas, not only compensating and repairing any biodiversity loss, but also creating a net benefit to the ecosystem.
Targeted action plan in line with TNFD (Task Force on Nature-Related Disclosure) guidelines.
2024 Results
WWF Biodiversity Risk Filter: Preliminary analysis of biodiversity risks in our plants and installation activities.
Prysmian sites potentially exposed to biodiversity-related risks.
Social Impact
We have always recognized that people are our most important asset. The history and success of our Group depend directly on the skills, commitment and motivation of our employees. We are committed to building a more equitable, inclusive and innovative world: that is why we have formalized our Social Ambition, focusing on promoting Diversity, Equity and Inclusion (DE&I), community support, employee engagement and skills development.
In addition, we actively engage with the local communities in which we operate to create shared value and foster their sustainable development. We continue to pursue ambitious goals, such as connecting millions of people by providing them with rapid digital access or power from renewable sources, ensuring broader and more inclusive access to sustainable resources. We are committed to reducing the digital divide and fostering inclusivity by ensuring that everyone can benefit from the opportunities provided by advanced connectivity.
Goals
Employee shareholders of Prysmian by 2028
Women employees hired by 2025
20/23%
Women executives by 2025
Injury rate among employees and externals by 2030
No. of households to which access to sustainable electricity can be provided by 2025
15 million
No. of households to which rapid digital access can be provided by 2025
Supply chain sustainability audits to be carried out in 2025
2024 Results
Employee shareholders of Prysmian
Women employees hired
19.2%
Women executives
Lost Time Injury Frequency (LTIF) rate
Households that have been provided with sustainable electricity
17.1 million
Households that have been provided with rapid digital access
Suppliers subject to sustainability audits from 2017 to 2024
Prysmian in ESG indices
| Index | 2022 | 2023 | 2024 |
|---|---|---|---|
 | Rank: 87/100 (ELQ World) included and ranked as 1st | Rank: 87/100 (EL World) included and ranked as 3rd | Rank 80/100 (EQL World) included and ranked 2nd in the World score |
 | Score: AA | Score: A | Score: A |
 | Score: 74/100 (Gold) | Score: 76/100 (Gold) | Score: 76/100 (Gold) |
 | Score Climate Change: B (World) Score Water Security: B | Score Climate Change: A- (World) Score Water Security: B | Score Climate Change: A- (World) Score Water Security: B |
 | Risk: 21,4 (Medium) | Risk: 16,5 (Low) | Risk: 16,1 (Low) |
 | Score: 3,8/5 | Score: 3,9/5 | Score: 4,0/5 |
 | Score: 63/100 | Score: 65/100 | Score: 61/100 |
 | Included (STOXX Italy 45 ESG-X e STOXX Europe 600 ESG-X) | Included (STOXX Italy 45 ESG-X e STOXX Europe 600 ESG-X) | Included (STOXX Italy 45 ESG-X e STOXX Europe 600 ESG-X) |
 | Included | Included | Included |
 | Rank: 57/100 | Rank: 58/100 | Rank: 58/100 |
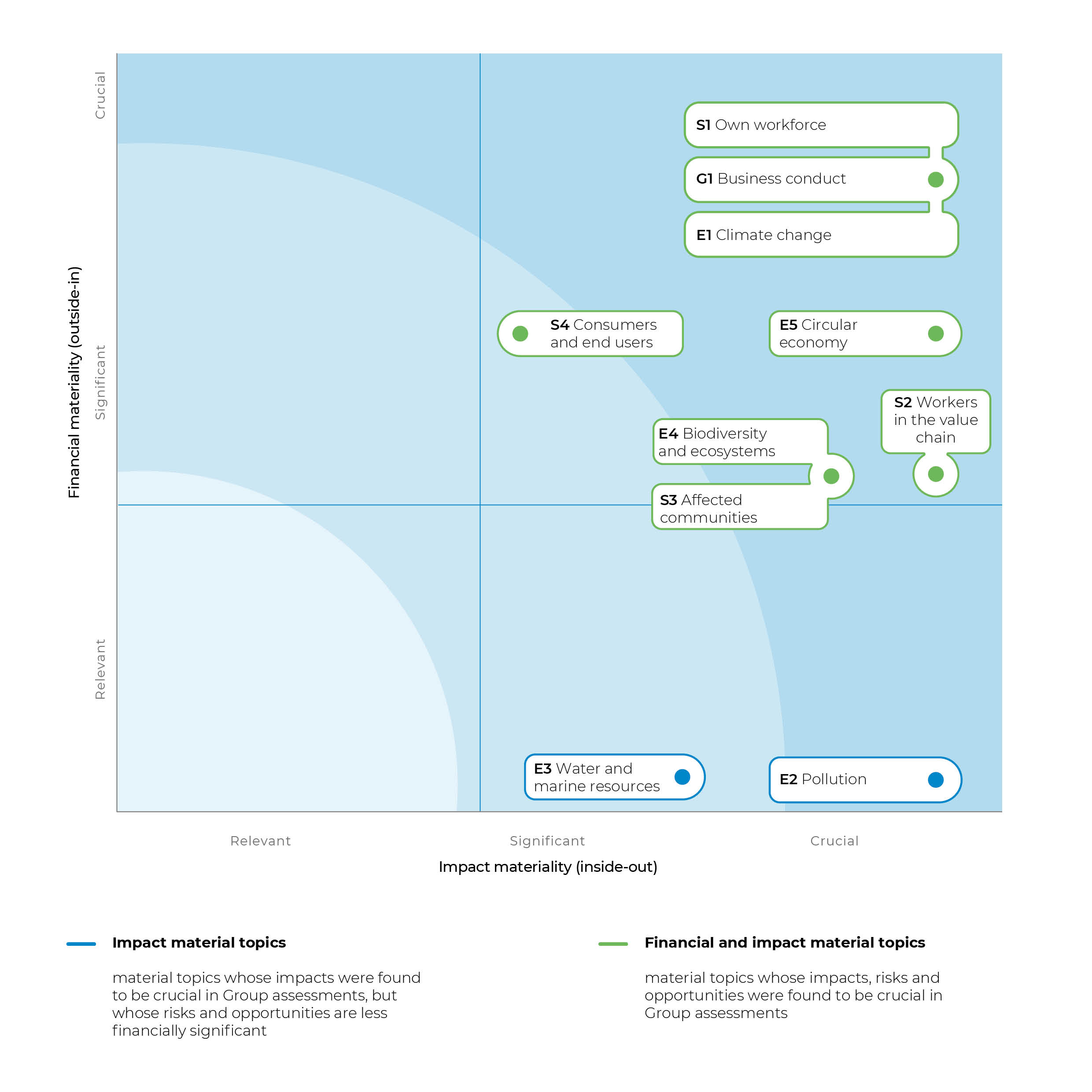
Materiality Matrix
Prysmian's dual materiality analysis is represented through a matrix that highlights the correlation between impact materiality and financial materiality. For each theme defined by ESRS, two aspects are considered: the impact the company has on the outside world, positioned on the x-axis, and the risk/opportunity that may affect the company's financial performance, positioned on the y-axis.
The matrix is structured to evaluate each theme according to two main dimensions:
- Impact materiality: represents the magnitude of the effect that the company’s activity generates or may generate on the environment, people and community, considering factors such as the geographic distribution of the impact, its irreversibility and the likelihood of its occurrence.
- Financial materiality: it measures the economic effect the issue in question may have on the company, both in terms of risks (such as unforeseen costs, penalties, reputational damage) and opportunities (e.g., economic benefits from adopting sustainable solutions or competitive advantages).
This visualization makes it easy to identify priorities for the company, directing efforts toward those issues that present the most significant combination of impact and financial materiality, and thus require immediate strategic attention:
- CLIMATE CHANGE (E1) OWN WORKFORCE (S1)
- BUSINESS CONDUCT (G1)
- CIRCULAR ECONOMY (E5)